tin tức nổi bật
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
-
 Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
-
Góp máy tính cho người khuyết tật
-
 Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
-
.jpg) Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
-
 Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
-
 Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
-
video người mù vượt qua bóng tối (P1) (năm 2012)
-
 Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
-
Tuyển dụng nhân viên làm tẩm quất ở Hoàng Kim
-
 Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
-
Biển tẩm quất người mù bị trịch thu vì ảnh hưởng đến làng văn hóa
-
 Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
-
.jpg) Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
-
 Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
-
 Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già

UNIT 4: CIVIL SERVICE MANAGEMENT (2)
Activity 11: Comprehension questions
- How many stages are there in the staffing process in the public service of Canada?
- What is an eligibility list?
- What is post-selection feedback?
Activity 12: Word study
Pair up the words so that they make logical units:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activity 13: Multiple choice
Read the following sentences and then decide which of the three answers A, B or C restates it, i.e. puts the information into other words:
- The responsibility for selecting candidates and appointing staff lies with the Public Service Commission.
(A). The Public Service Commission shifts responsibility for selecting candidates and appointing staff to someone else.
(B). The Public Service Commission has no responsibility for selecting candidates and appointing staff.
(C). The Public Service Commission bears responsibility for selecting candidates and appointing staff.
- Certain persons are given priority considerations.
- Person who are sure of themselves are considered first.
- Some categories of people are considered first
- People first consider what is sure to happen.
- Next the selection boards are set up and the process of screening and assessing candidates begins.
- After a selection board is established, candidates are shown on a screen.
- A selection board deals with sheltering candidates.
- A selection board tests candidates to see whether they are suitable for the job.
Activity 14: Summary
Summarize the text into 6 sentences:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- EXENSION
Activity 15: Conjunctions/ connectors
- Look at these examples taken from the texts:
- An overall focus on improved management of human resources, as well as improved development of those human resources, is an essential element.
- Government must decide how the staff will be organized and managed, therefore, the issues should be addressed through coherent policies.
- They are onformed in writing about the result of competition and they have the right to obtain further information about the selection process if they wish.
- Notes:
- Conjunctions are words like and, as well as, but, therefore, because, although. They are used to join clauses together, and to show the relationship between the ideas in the clauses.
- One conjunction is enough to join two clauses. Don’t use double conjunctions to join two clauses. (e.g. although the manager was tired, but he went to work).
- However, two conjunctions can be used to join three clauses (e.g. although the manager was tired, but he didn’t stay there long).
- Make one sentence from two. Use the work(s) in brackets in your sentences:
- Administration is as old as the state. Much debate is still going on about it. (although)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- My parents earn very little money. They are happy. (in spite of)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- The civil service is faced with a number of constraints and sluggishness. There is a requirement to reform it.( therefore)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- The merit system recognizes personnel management as an essential element of executive management. As such, personnel management can not be isolated from politics. (and)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………………………………
- The office is overstaffed. It is now in the process of cutting down the staff.( because)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- HOMEWORK
Exercise 1: Supplementary reading
Read the text carefully, then answer the questions that follow:
Issues in Human Resource Development in the Public Service
- Human resource development, a concept in public administration, introduces a new philosophy about human resources at both the national and organizational levels of concern: that a nation’s people as well as the personnel in public organizations are their most critical resources. Compared to non-human resources, human resources can produce more outputs in relation to inputs. This may be attributed to the creativity and innovativeness of the human resource which when applied to money, material, and technology convert these into desired outputs and outcomes. Non-human resources, however plentiful, cannot automatically convert themselves into outputs without the intervention of managerial and technical knowledge and skills of human resources.
- At the national level, human resource simply means people. The people of a countru are critical to its pursuit of national development. They play various roles: as change agents, beneficiaries, as well as constraints to development. Human resources development (HRD) involves the creation, development,, and improvement of the knowledge, attitudes, and skills of a people to prepare them for meaningful participation in the political, economic, social, cultural, and spiritual-moral aspects of their individual as well as national lives.
- Human resource development prepares people for active and meaningful participation in the political process of leader selection and in the formulation of policy decisions affecting their lives. It equips them with knowledge and skill so that they can be gainfully employed and economically self-sufficient and thus gain self respect and dignity. It develops social attributes which will enable them to cope with the requirements and pressures of social life and make them acceptable to the society and community. HRD prepares people to identify themselves with and be proud of their culture, their art, and their history. Finally, HRD prepares people for a morally and spiritually upright way of life (Harbison and Myers, 19464).
- At the organizational level, HRD paves the way for adequate and fair recruitment, training and development, including motivation, utilization and conservation of human resources in organizations. Organizational effectiveness depends on the capability and competency of the personnel responsible for implementing the organization’s policies, programs and projects and in the delivery of goods and services to its clientele and beneficiaries.
- The HRD philosophy provides for a personnel management system that ensures a developmental and systematic treatment of employee concents. Unlike the traditional personnel management system which focuses more on rules and processes for personnel actions and transactions, the developmental system’s major forcus in human resources is organization.
- The public bureaucracy is the center stage for human resource development which, however, does not exist in a vacuum. It is directly conditioned and affected by its contextual environment. The societal and political culture obtaining within definite time periods under a specific political system and leadership set the contextual realities under which bureaucracy develops its distinct administrative culture. The different variants, in turn, determine the characteristics and qualities of the bureaucracy’s human resources.
- Recent events in many developing countries show a shift from authoritarianism to democracy; and from traditionalism to modernization. However, the experience towards modernization is marred by a growing dependency on foreign loans and technical assistance which, sometimes, results in people carrying the burden of development rather than enjoying its fruits as beneficiaries. Often, the rapid changes and redevelopment of national resources place challenging pressures on the human resource development function. How to avoid the unintended consequences of development like poverty and a lowering of the people’s standard of living is a real problem faced by HRD decision-makers.
- Governments are, today, confronted with competing HRD issures, namely: (1) avoiding conflict and the searching for balance between merit and political patronage in public service employment; (2) increasing size of the bureaucracy; (3) sustaining personnel motivation and morale to ensure positive work behavior and high levels of performance; and (4) continuing training and development of civil servants to equip them with the necessary knowledge, attitudes, and skills to meet the present and future challenges of public service.
Answer the following questions:
- In what ways do human resources differ from non-human resources?
- What is meant by human resource development (HRD)?
- What are the aims of HRD?
- What role does HRD play at the organizational level?
- How does HRD philosophy differ from the traditional personnel management system?
- Explain why “ The public bureaucracy is the center stage for human resource development which, however, does not exist in a vacuum.”
- What is the real problem that HRD decision- makers in developing countries are faced with?
- What are competing HRD issues with which governments are, today, confronted?
- REVIEW TEST
You have 20 minutes to complete the following test. When you have finished, your teacher will give you the key and you will mark your own answer.
Test 1: Questions and auxiliary verbs
Write questions for the following statements:
- An important aspect of effective public administration is efficient management of human resources through an appropriate civil service system.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………?
- The government should re- define the role of the public sector in the light of its political objectives, its resources and the real capacity of its public service.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………?
- The civil service needs to focus in achieving programmed goal.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..?
- The Public Service Commission has the responsibility for selecting candidates and appointing staff.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………?
(4 points)
Test 2: Translation into Vietnamese
- Another source of expansion of public bureaucracies is the legislature.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- In response to the demands of their constituents, legislators pass laws which launch new policies and programs addressing problems for which the voters press for resolution.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Sometimes, such laws provide for new administrative structures to carry out the policies and programs.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(6 points)
Ý kiến độc giả
Các tin liên quan
- UNIT 1: ADMINISTRATION – PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (1)
- UNIT 1: ADMINISTRATION – PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (2)
- UNIT 2: GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (1)
- UNIT 2: GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (2)
- UNIT 3: DEFINING MANAGEMENT (1)
- UNIT 3: DEFINING MANAGEMENT (2)
- UNIT 4: CIVIL SERVICE MANAGEMENT (1)
- UNIT5: PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION REFORM (1)
- UNIT5: PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION REFORM (2)
Ảnh & vi deo sự kiện
-

Dự án tài trợ máy xông hơi cho Hội ng...
-

Hoàng Kim ra mắt Công ty cổ phần tư v...
-
Sinh nhật Website Hoàng Kim tròn 1 tu...
-

Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim với công...
-
Kỷ niệm ngày người khuyết tật Việt na...
-
.jpg)
Tổng kết năm 2010 của Trung tâm Hoàng...
-
Tin nhanh
-
.jpg)
Sản phẩm - Dịch vụ
-
Khách hàng thân thiện
-

Nhân viên Hoàng Kim
tin tức mới
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
-
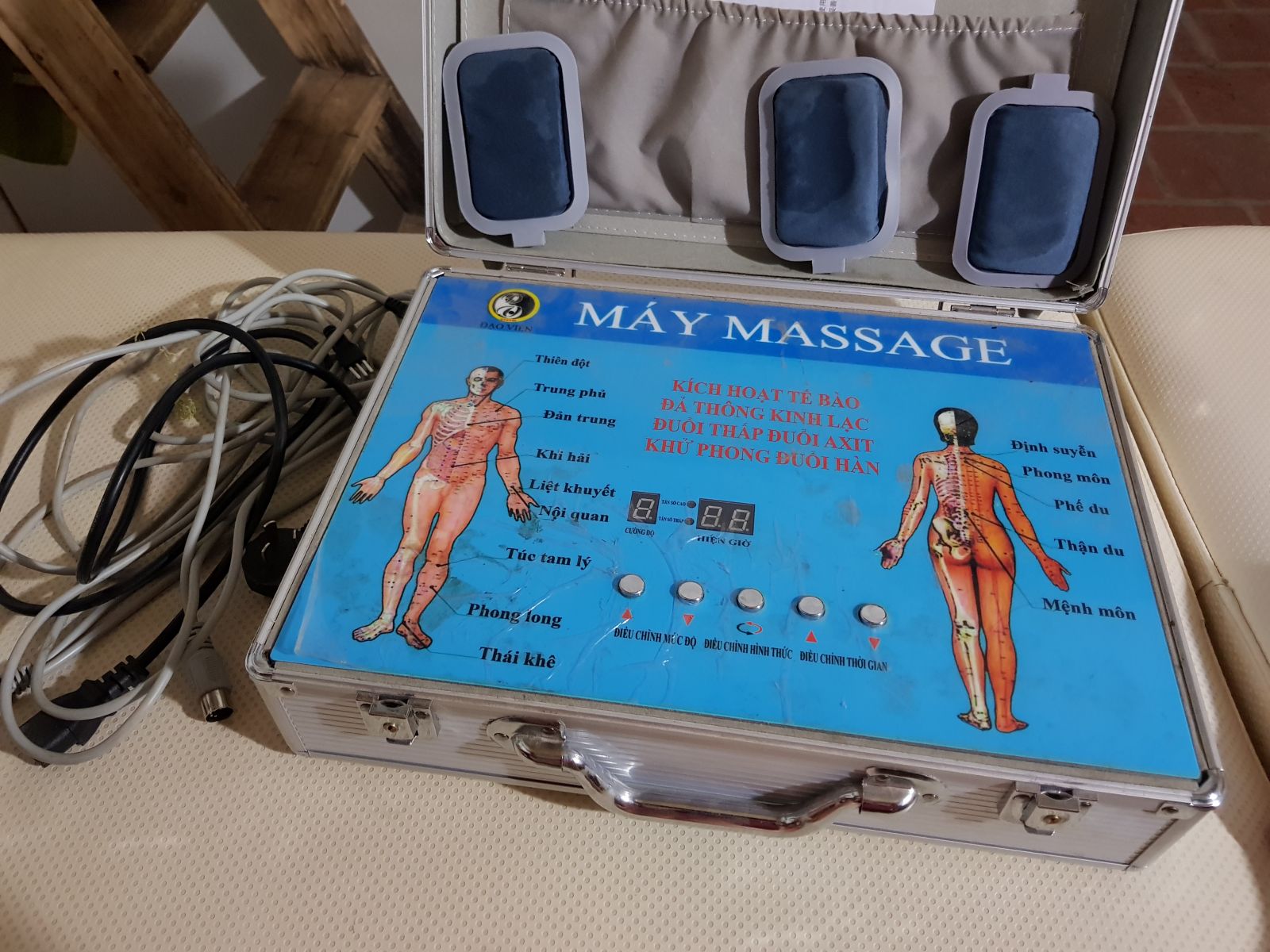 Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
tin tức xem nhiều
-
 Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
-
 Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
-
 Dịch vụ đăng quảng cáo đặt Banner giá rẻ - Hiệu quả bất ngờ
Dịch vụ đăng quảng cáo đặt Banner giá rẻ - Hiệu quả bất ngờ
-
 Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Ủng hộ từ thiện






.JPG)

.JPG)








Bình luận