tin tức nổi bật
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
-
 Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
-
Góp máy tính cho người khuyết tật
-
 Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
-
.jpg) Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
-
 Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
-
 Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
-
video người mù vượt qua bóng tối (P1) (năm 2012)
-
 Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
-
Tuyển dụng nhân viên làm tẩm quất ở Hoàng Kim
-
 Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
-
Biển tẩm quất người mù bị trịch thu vì ảnh hưởng đến làng văn hóa
-
 Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
-
.jpg) Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
-
 Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
-
 Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già

UNIT 2: GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (2)
Activity 12: Pronunciation practice
Mark the stress and intonation in the following sentences and then read them aloud:
- Governance and development are currently viewed as intertwined.\
- Development is no longer solely a matter of economics.
- There is a wide desire for participation in the government.
- The reform of government often goes hand in hand with economic reform.
- It is usually good government that is likely to institutionalize democracy through fair elections.
- EXTENSION
Activity 12: Pre-reading of Text 2
Match the words and expressions on the left with their definitions on the right:
|
1.pedominantly
2. impact 3. counterproductive 4. import substitution
5. irrigation 6. to reveal 7. dissemination 8. interventions |
a.(instances of) interference or becoming involved b. supplying (land, crops) with water c. for the most part; mainly d. having the opposite effect to that intended e. to make (facts etc.) known f. strong effect on sth. g. support for struggling industry h. spreading (ideas, beliefs etc.) widely |
Activity 13: Text 2
a. Skim through the text to get a general understanding about the topic (note that the numbers are line numbers)
Strategies for Sustainable Growth and Equity
- Poverty in Asia is predominantly rural. Macro-economic policies are generally viewed to be the most important contributors to economic growth in developing countries. Their impact on poverty, though, is rarely analyzed. Typically, higher growth rates reduce absolute levels of poverty but the application of too extensive distribution policies can be counterproductive.
- High productivity of the agricultural sector is very important for reducing poverty. In countries where land is limited and agriculturally-led growth policies are not feasible, consideration should be given to public works policies as an alternative option.
10. Import substitution polices failed in Asian countries because they became a permanent protection for inefficient industries. Access to land, irrigation, credit, agricultural extension and market-based pricing policies, underpinned by good institutional mechanisms, can facilitate improvements in agricultural productivity.
15. Without good government none of the best intended policies can be effectively implemented. Experience from the Asia region has indeed revealed a positive correlation between economic growth and poverty alleviation and the quality of public administration.
- To advance regional cooperation, UNDP could promote information dissemination on macro-economic policies and micro-level interventions that have proven to be effective in alleviating poverty in Asian countries.
- Read the text again and look at the following questions:
- What are considered to be the most important contributors to economic growth in developing countries?
- What happens when the growth rates get higher?
- Which sector is most likely to contribute to reducing poverty?
- Why did import substitution policies fall in Asian countries?
- Can the best intended policies be effectively implemented without good governance?
Activity 14:
- Read the text again to mark on which line(s) you find the answer to each question. The first answer is given as an example:
|
Question |
Line |
|
1 |
1 + 2 |
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
|
- Answer the question in writing. Don’t copy sentences directly from the text:
Question 1: ........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
Question 2: ........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
Question 3: ........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
Question 4: ........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
Question 5: ........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Individual/pair work. Summarize the text in 5 sentences:
1. ........................................................................................................................................................
2. ........................................................................................................................................................
3. ........................................................................................................................................................
4. ........................................................................................................................................................
5. ........................................................................................................................................................
f.Class work: Present your summary before the class.
D. HOMEWORK
Exercise 1: Complementary reading
Read the following text and answers the questions at its end:
Administrative and Financial Decentralization. Contemporary challenges such as urbanization, the need for enhanced gender equality in governance and effective protection of the environment all require increasingly holistic approaches. In dealing with these important issues, decentralization of government tasks and functions has a number of advantages. Enhanced efficiency and effectiveness in decision-making and resource utilization and better accountability and responsiveness are important benefits of decentralization. A decentralized system of governance should promote enhanced political stability, more balance growth, effective and efficient service delivery, and appropriate balance of power between central and local governments and grassroots participation in decision-making. The degree of decentralization, however, will vary according to local needs, requirements and capabilities. In the view of some participants, the necessary conditions for decentralization were not yet in place for their countries. A number of constraints impeding decentralization were identified such as general lack of capacity of local government and civil society.
Civil Society – Government Cooperation in Poverty Alleviation. The general experience with government-run poverty alleviation programmes in Asia has not been encouraging. This dissatisfying performance is of particular importance as the levels of poverty are on the increase despite economic success in many Asian countries. To improve the performance of these programmes, Asian governments are increasingly entering into partnerships with civil society organizations (CSOs). It is important for CSOs to build up a reputation for being responsive to community and government requests, for transparent handling of donor funds and for complementing government action rather than duplicating it. Mistrust often exists between these two parties due to lack of information about each other’s role and goals and because of perceived competition for financial resources. However, the Asian experience demonstrates many encouraging examples of civil society – government cooperation in poverty alleviation.
Capacity of Management Training Institutions. The preconditions for strengthening the effectiveness of management training institutions in the region were identified as enhanced resource mobilization, a proper management structure and the effective use of a strategic development programme to guide the operation of these institutions. Only in Malaysia and Japan do such institutions appear to have adequate governmental support. However, management training institutions will increasingly have to seek collaboration with the private sector by tailoring courses that meet its needs, offering consultancy services, conferring degrees and undertaking research. Malaysia provides a good example of a country in which government management training institutions have been able to foster a close relationship with the private sector. Poor governance and leadership have become significant constraints to enhancing the capacity of such institutions. There is a great need to update the syllabuses and curricula of training institutions and to make them more innovative.
Legal and Political Impediments to Gender Equality in Governance. Despite Asia’s impressive economic growth rate and significant national investments in basic social services, poverty and gender inequality remain pervasive throughout the region. These inequalities are compounded by various types of political and legal impediments to women’s participation in governance. Women make immense contributions to society and economic activities, many of which are not accounted for in traditional national accounts. Women’s entry into political and legal structures in sufficient number is likely to transform the processes and institutions of governance. Women’s participation in governance, however, is impeded by a number of factors such as people’s mindsets; limited access to education; legal constraints; women’s passiveness and a lack of machinery for the advancement of women. To improve the status of women, participants recommended the following actions: electoral and institutional reforms (e.g. establishment of a Ministry of Women’s Affairs and/or a quota system); integration of a gender dimension in development planning; improved access for women to education and removal of various legal impediments to forming groups.
Changing Role of the State in Promoting Participatory Development. The concept of development has moved from a preoccupation with economic growth to a focus on people, particularly the satisfaction of the basic needs of the poor. In this context, the state enables by providing the development vision, legal and regulatory framework and political order within which firms and organizations can plan and act. An enabling state is not restrictive but regulative and supportive. The state can promote more participatory development by recognizing outstanding performances by NGOs and by setting up consultative bodies to foster such collaboration. The state should provide strategic guidance and promote the work of NGOs through regulation and legislation especially in areas where the capacity of the state is weak. NGOs can also serve as a vehicle to empower women and strengthen their participation in the development and political process. The state could further promote participatory development by articulating a clear vision and strategy for development, developed through consensus at all levels. NGOs could foster this development by ensuring that their objectives are compatible with national goals.
Changing Role of the State in Promoting Private Sector Development. The Asian experience demonstrates some very good examples where the private sector has been an important contributor to economic and social development. In other Asian countries, however, the involvement of the private sector has been much less effective. The main explanation for the significant variations in economic and social performance in countries of the Asia region appears to be their different systems of governance. What is needed in the slower growing Asian countries is to create a dynamic relationship between effective government policies and the private sector. In order to revive the private sector in these countries, governments need to undertake a number of measures, including the promotion of a dialogue between the private sector and the government and the establishment of a well-functioning system of property rights and a judicial system for arbitration.
Answer the following questions:
- What are benefits of administrative and financial decentralization?
- There are problems when governments are entering into partnerships with civil society organizations (CSOs). Why is it important to involve CSOs in the development process?
- In what ways can the capacity of management training institutions be improved?
- What are impediments to women’s participation in governance? How could one improve the status of women?
- Can you explain the new role of the state as an enabling state in the development process?
- What do government need to do to revive the private sector in their countries?
E. REVIEW TEST
You have 30 minutes to complete the following test. When you have finished, your teacher will give you the key and you will mark your own answer.
Test 1: Vietnamese-English translation
- Sựtăng trưởng kinh tếđòi hỏi (require) sựphối hợp của nhiều ngành.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Nhiều nước đang phát triển có những chiến lược phát triển rất tốt.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Sựcải tổchính phủphải đi đôi với (go hand in hand with) sựcải thiện kinh tế
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Một chính phủđã được cải tổthường mang lại sựổn định chính trị.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Chính phủViệt Nam ban hành những chính sách kinh tếthịtrường theo định hướng xã hội chủnghĩa.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
(2.5 points)
Test 2: English-Vietnamese translation
1. The goals of development, democracy and political stability may appear to be in conflict at times.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
2. An efficient government machine and support generated to economic reform sustain development efforts.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
3. A good government is likely to institutionalize democracy through fair elections.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
4. Governance always refers to the highest level of decision-making.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
5. Governance refers to the exercise of constitutional authority to manage state affairs.
...........................................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................................
(2.5 points)
Test 3: Write complete sentences
- governance/synonymous with/ good government
...........................................................................................................................................................
- There be/variation/understanding/term/governance
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Reformed government/provide/political stability
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Good government/provide/impartial judiciary/to guarantee/rule of law
...........................................................................................................................................................
- Good government/arrange/good social services
...........................................................................................................................................................
(5points)
Ý kiến độc giả
Các tin liên quan
- UNIT 1: ADMINISTRATION – PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (1)
- UNIT 1: ADMINISTRATION – PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (2)
- UNIT 2: GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION (1)
- UNIT 3: DEFINING MANAGEMENT (1)
- UNIT 3: DEFINING MANAGEMENT (2)
- UNIT 4: CIVIL SERVICE MANAGEMENT (1)
- UNIT 4: CIVIL SERVICE MANAGEMENT (2)
- UNIT5: PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION REFORM (1)
- UNIT5: PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION REFORM (2)
Ảnh & vi deo sự kiện
-

Dự án tài trợ máy xông hơi cho Hội ng...
-

Hoàng Kim ra mắt Công ty cổ phần tư v...
-
Sinh nhật Website Hoàng Kim tròn 1 tu...
-

Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim với công...
-
Kỷ niệm ngày người khuyết tật Việt na...
-
.jpg)
Tổng kết năm 2010 của Trung tâm Hoàng...
-
Tin nhanh
-
.jpg)
Sản phẩm - Dịch vụ
-
Khách hàng thân thiện
-

Nhân viên Hoàng Kim
tin tức mới
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
-
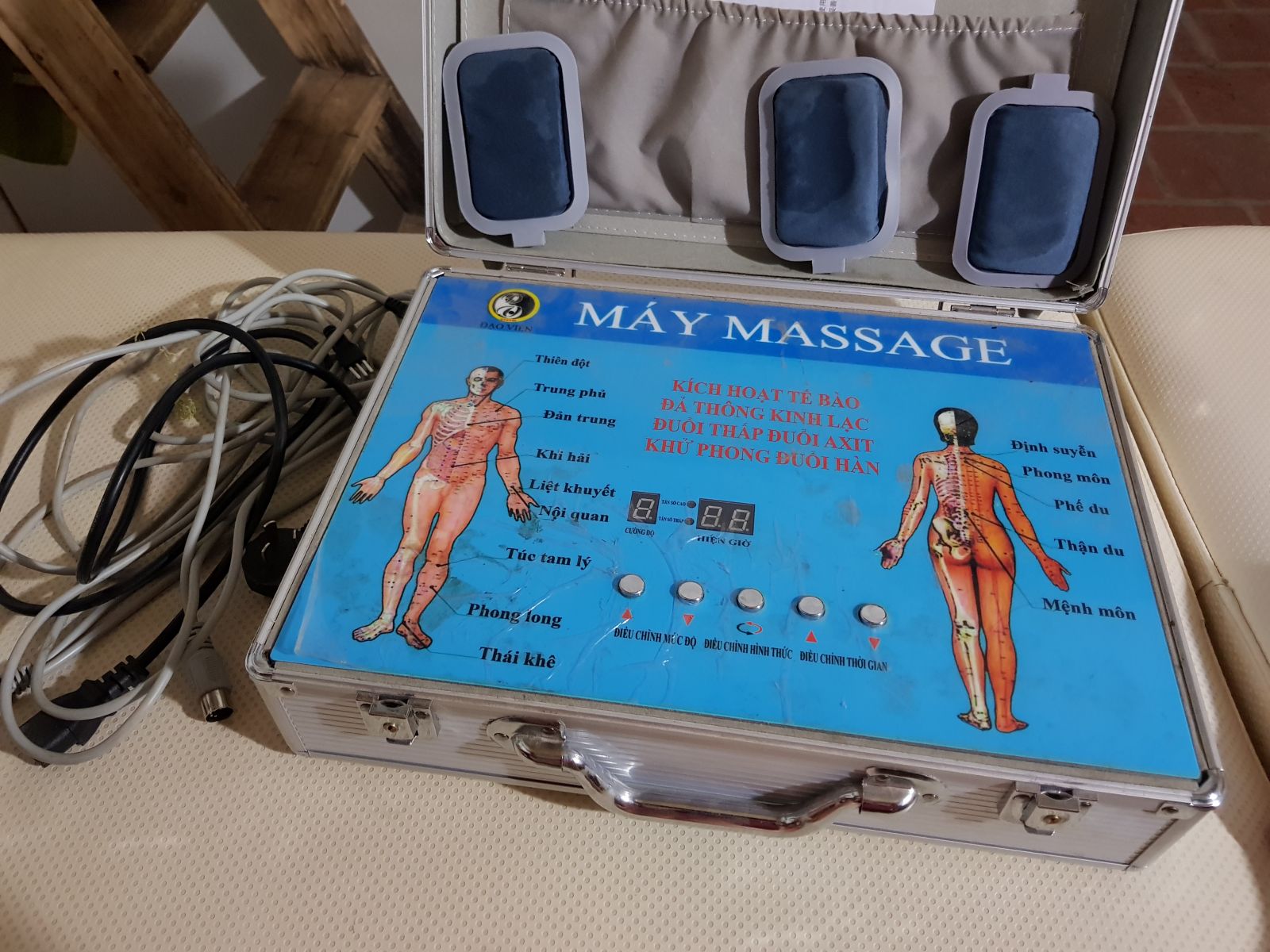 Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
tin tức xem nhiều
-
 Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
-
 Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
-
 Dịch vụ đăng quảng cáo đặt Banner giá rẻ - Hiệu quả bất ngờ
Dịch vụ đăng quảng cáo đặt Banner giá rẻ - Hiệu quả bất ngờ
-
 Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Ủng hộ từ thiện






.JPG)

.JPG)








Bình luận