tin tức nổi bật
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
Hoàng Kim Massage thông kinh lạc toàn thân thải độc tố cơ thể, phục hồi sức khỏe, thổi bay những cơn đau bằng Công nghệ điện sinh học DDS
-
 Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim tổ chức lớp Tập huấn kỹ thuật massage làm đẹp da mặt, massage giảm mỡ bụng cạo gió, giác hơi ống trúc cho nhân viên
-
Góp máy tính cho người khuyết tật
-
 Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
Chương trình tài trợ 1000 máy xông hơi cho thành viên hội người mù việt nam
-
.jpg) Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
Những ngón tay dệt nên thần thoại
-
 Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
Quyển sách: Món ngon ngày tết
-
 Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
Giám đốc Trung tâm Hoàng Kim được ghi nhận là thành viên tích cực của Hiệp hội thương mại điện tử Việt Nam (năm 2012)
-
video người mù vượt qua bóng tối (P1) (năm 2012)
-
 Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
Giới thiệu 2: Đĩa âm nhạc tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim
-
Tuyển dụng nhân viên làm tẩm quất ở Hoàng Kim
-
 Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
Người giàu không ở... hai con mắt
-
Biển tẩm quất người mù bị trịch thu vì ảnh hưởng đến làng văn hóa
-
 Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
Những ngón đàn xuyên suốt màn đêm
-
.jpg) Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
Hoàng kim trước thềm xuân mới.
-
 Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
Massage của người khiếm thị từ góc nhìn của một người “ngoại đạo”
-
 Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già
Xoa xát mắt để phòng cận thị và hoa mắt ở tuổi già

UNIT 9: Auxiliary verbs (trợ động từ) and sentence types (loại câu)
Topic 8: The Body (cơ thể)
I. Auxiliary verbs
- Auxiliary verbs are: “to be”, “to do” and “to have”. (trợ động từ gồm: “to be”, “to do”, “to have”)
- use them together with a main verb to add extra meaning to a sentence, to form a question, a negative sentence, a perfect tense… (dùng chúng với động từ chính để bổ sung ý nghĩa cho câu văn, để viết câu hỏi, câu phủ định, thì hoàn thành...)
- auxiliary verbs can be main verbs (trợ động từ có thể là động từ chính)
1. To be (auxiliary and main verb)
- Examples main verb (ví dụ động từ chính)
- I am tall.
- They are fat.
- Examples auxiliary(ví dụ trợ động từ): The school is out. (trường học đã nghỉ)
auxiliary: is (trợ động từ: is)
2. To do (auxiliary and main verb)
- used in negative sentences and questions in simple present/past, use the infinitive of the main verb (dùng trong câu phủ định và câu hỏi trong thì hiện tại/quá khứ đơn, dùng dạng nguyên thể của động từ)
- Examples main verb
- She does her homework (cô ấy làm bài tập)
- You do this exercise. (bạn làm bài tập này)
- Examples auxiliary
- Does she do her homework? –does: auxiliary, do: main verb
(cô ấy làm bài tập chưa?)
- Do you understand this exercise? –do: auxiliary, understand: main verb
(bạn có hiểu bài tập này không?)
3. To have (auxiliary and main verb)
- Examples main verb: I have a round face.
- Examples auxiliary: I have got white teeth.
Have: auxiliary, got: main verb
II. Exercises
1. Choose the best form
- I do / does / have / has not like my nose..
- Do / does / have / has she know that you are so small?
- Do / does / have / has you drink milk?
- It do / does / have / has not matter.
- They do / does / have / has not want to play outside.
2. Auxiliary or main verb?
- I am thin.
- They have got blonde and long hair.
- We do not know his face.
- My friend Amy does have very long legs.
- What is this?
- Does he speak English?
- Mary has beautiful blue eyes.
III. TOPIC 8: The Body (cơ thể)
1. Describe a person. (miêu tả một người)
a) Michael is a boxer. (Michael là một võ sĩ quyền Anh)
He is short (anh ấy lùn)
He is fat. (anh ấy béo)
He is heavy. (anh ấy nặng cân)
He is strong. (anh ấy khỏe)
b) She is a ballerina. (cô ấy là một nữ diễn viên ba lê)
She is young. (cô ấy trẻ)
She is not old. (cô ấy không già)
She is tall. (cô ấy cao)
She is thin. (cô ấy gầy)
She is light. (cô ấy nhẹ cân)
But she is not weak. (nhưng cô ấy không yếu)
She is strong. (cô ấy rất khỏe)
2. Describe a face (miêu tả khuôn mặt)
- a round face: mặt tròn
- an oval face: mặt trái xoan
- full lips: môi dày
- thin lips: môi mỏng
- long hair: tóc dài
- short hair: tóc ngắn
3. Exercise
a) Read.
Miss Lily is tall and thin. (cô Lily cao và gầy)
She has a round face. (cô ấy có khuôn mặt tròn)
She has long blonde hair. (cô ấy có mái tóc dài màu vàng)
She has brown eyes. (cô ấy có đôi mắt nâu)
She has a small nose. (cô ấy có mũi nhỏ)
She has full lips and small white teeth. (cô ấy có môi dày và hàm răng trắng nhỏ)
b) Answer the questions
- Is Miss Lily’s face oval or round?
- Is Miss Lily’s hair long or short?
- What colour is her hair?
- Are her lips full or thin?
- What colour are her eyes?
- Is her nose big or small?
c) Make questions with “What colour” and answer.
Example: her hair/black
What colour is her hair? –It’s black.
- Mary’s eyes/green.
- Mr. Minh’s hair/grey
- Children’s teeth/white
- Your school/yellow
- Her lips/red
d) Describe your body from your head to your feet.
(miêu tả cơ thể bạn từ đầu đến chân)
e) Describe your mother, your father, your brother, your sister, your friends, your classmates, your teacher...
IV. Sentence types
There are four sentence types:
- Statement
- Question
- imperative/command
- exclamation
(bốn loại câu gồm: câu trần thuật, câu hỏi, câu cầu khiến/yêu cầu và câu cảm thán)
1. Statement (câu trần thuật)
a. In a positive statement (trong câu trần thuật khẳng định)
subject-verb-object (S-V-O).
- Examples:
- I speak English.
- I play football.
- Watch out!
The place and the time can come after the object.
(thời gian và địa điểm có thể theo sau tân ngữ)
- Examples:
- I have breakfast in the kitchen.
- John goes to church on Sunday.
b. In a negative statement (trong câu trần thuật phủ định)
subject-(auxiliary verb)-not-verb-object-place-time.
- Examples:
- Katy doesn’t use the computer in her room.
- Mika does not speak English.
2. Questions (câu hỏi)
- Examples: Do you like fighting?
- Yes/No questions:
- Answer this question with “yes” or “no”. (trả lời câu hỏi này với “yes” hoặc “no”)
Statement: Nancy likes Pizza.
Question: Does Nancy like Pizza?
- Watch out!
- When you have an auxiliary verb in the statement then you use it as the question word. (khi có trợ động từ trong câu cảm thán, sử dụng nó như từ để hỏi)
- When you have no auxiliary verb in the statement then you use “do” as the question word. (khi không có trợ động từ trong câu cảm thán sử dụng “do” là từ để hỏi)
- Examples:
- Does Tam like elephants?
- Do John and Frank live in Hanoi?
- form negative questions with the negative auxiliary verb. (viết câu hỏi với trợ động từ dạng phủ định)
- Examples:
- Isn´t Arlette here today?
- Doesn’t he like blue eyes?
b. Questions with question words (câu hỏi với các từ để hỏi)
Question words are always in the first position. (từ để hỏi luôn đứng ở vị trí đầu câu)
- Who?
- Examples:
- Who do you like? (bạn thích ai?)
- Who learns Russian? (ai học tiếng Nga?)
- What?
- Examples:
- What does he do at the weekends? (Anh ta làm gì vào cuối tuần?
- What is that?
- What time?
- What time is it? (Mấy giờ rồi?)
- At what time does the class start? (lớp học bắt đầu vào lúc mấy giờ?)
- When?
- Examples:
- When do we have history? (khi nào chúng ta học lịch sử?)
- When does she go to school? (khi nào cô ấy đến trường?)
- Where?
- Examples:
- Where do you live?
- Where is your school?
- How
- Example:
- How are you?
- How about you? (thế còn bạn?)
- How much/How many:
- Example:
- How much does it cost? (cái này giá bao nhiêu?).
- How many people are in your family? (có bao nhiêu người trong nhà bạn?)
- How long? (bao lâu)
How long is the film? (bộ phim kéo dài bao lâu?)
- How far? (bao xa)
How far is your house from the school? (từ nhà bạn đến trường bao xa?)
- Which?
Which book do you want? (bạn muốn quyển sánh nào?)
Which girl comes to the celebration? (Cô gái nào đến dự buổi lễ?)
- Whose?
Whose car is this? (xe này của ai?)
- Whom:
To whom do you talk? (bạn nói chuyện với ai thế?)
- Why?
Why are you late? (tại sao bạn lại muộn?)
3. Imperative /command (yêu cầu, cầu khiến)
- Example:
- Wait a moment, please. (xin đợi một chút).
- Don´t forget the English lesson! (đừng quên buổi học tiếng Anh).
- Open the door, please!
- Close the door, please!
- You use the imperative when you want that somebody does something.
(sử dụng câu cầu khiến khi muốn ai đó làm gì đó)
- Examples:
- Listen! (hãy lắng nghe).
- Sit down, please! (hãy ngồi xuống).
- Negative imperative: do not (don´t).
(dạng cầu khiến phủ định: do not (don’t)
Don´t do this. (đừng làm cái này).
- You also can use “let´s” (let us) for an imperative sentence.
(sử dụng let’s (let us) cho câu cầu khiến)
- Examples:
- Let´s go to a disco. (đi sàn nhảy đi)
- Let´s not fight / Don´t let us fight. (đừng đánh nhau)
4. Exclamation (câu cảm thán)
Exclamations tell about strong feelings of the speaker, like happiness, sadness, anger … at the end of an exclamation you use an exclamation mark. (câu cảm thán thể hiện ấn tượng mạnh của người nói như sự hạnh phúc, buồn, giận dữ… Cuối câu cảm thán luôn dùng dấu chấm than)
- Examples:
- How nice to see you!
- Fantastic!
- That’s great!
- What a bad accident!
V. Exercises
1. Make statements with these words and then form the negative statement and a question.
(viết câu trần thuật với những từ dưới đây sau đó viết dạng phủ định và câu hỏi)
- Example: Sandra/to go/to school.
Sandra goes to school.
Sandra doesn’t go to school.
Does Sandra go to school?
- Tom/to do/sports.
- They/to watch/TV.
- You/to see/my parents.
- Mandy/to live/in London.
2. Ask for the words in capital letters. (hỏi cho những từ được in hoa)
- It’s SIX O’CLOCK.
- My birthday is IN OCTOBER.
- She lives in LONDON.
- Jack is FINE.
- This chair costs 100 DOLLARS.
- In her room there are SEVEN children.
- IN HER ROOM there are seven children.
- In her room there are seven CHILDREN.
- The film is 3 HOURS long.
- My house is 4 MIN far from here.
- They want THE BLUE COMPUTER.
- MANDY is my sister.
- I’m good in English BECAUSE I LEARN SO MUCH.
- I talk to MY BROTHER.
- This is THEIR calendar.
- That is A CAR.
3. Make exclamation examples with adjectives (lấy ví dụ về câu cảm thán với các tính từ): beautiful, angry, bad, long …
Ý kiến độc giả
Các tin liên quan
- UNIT 1: Let’s learn English (học tiếng Anh)
- UNIT 2: Personal pronouns and ”to be”
- UNIT 3: Numbers (số)
- UNIT 4: Possessives (sở hữu) and "this, that, these, those”
- UNIT 5: Singular and plural (số ít và số nhiều)
- UNIT 6: Reflexives (đại từ phản thân)
- UNIT 7: Articles (mạo từ)
- UNIT 8: My day
- UNIT 10: Present simple
- UNIT 11: Prepositions (giới từ)
Ảnh & vi deo sự kiện
-

Dự án tài trợ máy xông hơi cho Hội ng...
-

Hoàng Kim ra mắt Công ty cổ phần tư v...
-
Sinh nhật Website Hoàng Kim tròn 1 tu...
-

Tẩm quất người mù Hoàng Kim với công...
-
Kỷ niệm ngày người khuyết tật Việt na...
-
.jpg)
Tổng kết năm 2010 của Trung tâm Hoàng...
-
Tin nhanh
-
.jpg)
Sản phẩm - Dịch vụ
-
Khách hàng thân thiện
-

Nhân viên Hoàng Kim
tin tức mới
-
 Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
Hoàng Xuân Hạnh - Hoàng Kim: Doanh nhân người khiếm thị được biểu dương năm 2018
-
 Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
Doanh nhân khiếm thị tâm huyết / Chàng trai khiếm thị thành lập doanh nghiệp hỗ trợ nghề
-
 Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Tôi mách bạn 6 Giải pháp hàng đầu để trở thành chuyên gia trong trị liệu: chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
-
 Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
Giáo trình dạy học DDS – Điện sinh học
-
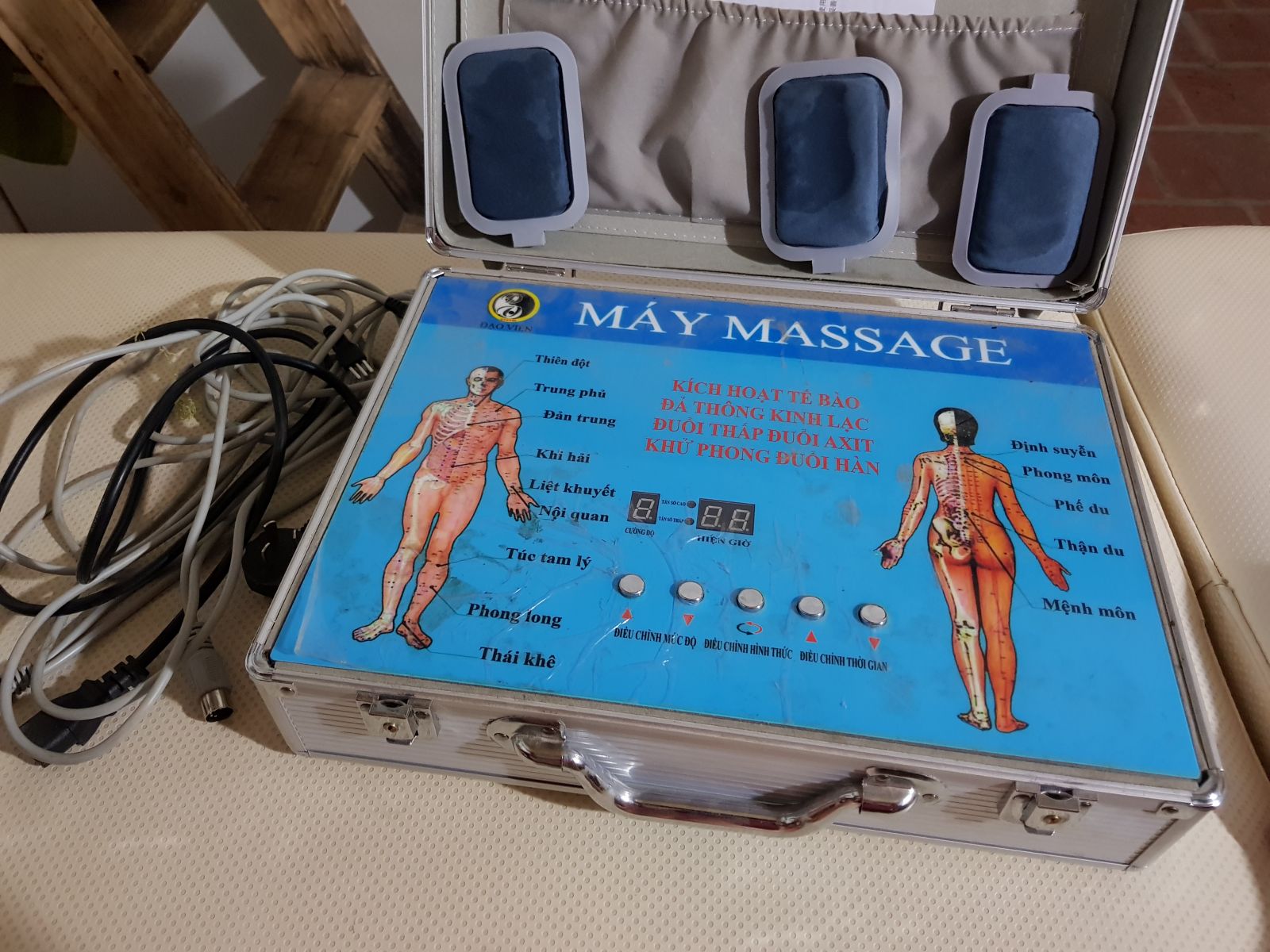 Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
Ưu thế nổi bật của công nghệ DDS – Điện sinh học trong chữa bệnh và làm đẹp
tin tức xem nhiều
Ủng hộ từ thiện






.JPG)

.JPG)









Bình luận